News
UGC Bill 2026 Sparks Controversy Across India's Campuses
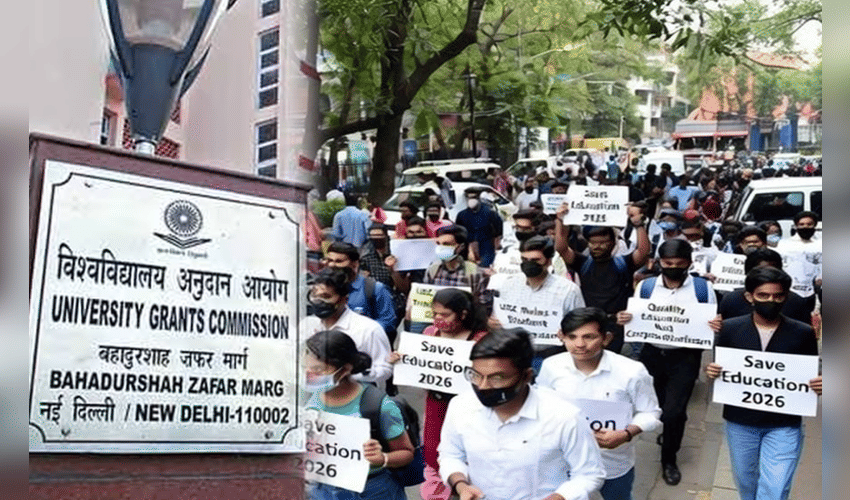

The University Grants Commission (UGC) has introduced the UGC Bill 2026, a sweeping set of regulations aimed at promoting equity and preventing discrimination across universities and colleges in India. The move has immediately captured national attention, with supporters calling it a landmark step toward inclusive education, while critics warn it could lead to misuse, campus tensions, and legal disputes.
According to the new regulations, all higher education institutions will be required to establish Equity Committees and Equal Opportunity Centres to handle complaints of discrimination and harassment. These institutions must also maintain 24×7 grievance reporting channels to ensure that students and staff facing bias based on caste, gender, religion, disability, or other factors have a clear path to seek redress. The UGC has emphasized that the bill is designed to create safer and fairer campuses, aligning with the principles outlined in the National Education Policy 2020 and previous Supreme Court directives on equality in education.
Government officials argue that the bill will empower marginalized students and faculty by providing structured grievance mechanisms that were previously missing in many colleges. Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan stated that the regulations are intended to ensure that “every student and faculty member can study and work in an environment free from discrimination, harassment, or exclusion.” Supporters also point out that the bill will help institutions respond more effectively to reports of bias and create a culture of accountability across campuses.
The UGC Bill 2026 has sparked immediate protests and criticism. Many student organizations, alumni groups, and political voices have raised concerns that the bill’s broad definitions of discrimination could open the door for misuse, allowing frivolous complaints or politically motivated actions. There is also a debate over the exclusion of general category students from certain protections, which some fear could foster reverse discrimination and social tension on campuses. Demonstrations have erupted in several cities, and petitions challenging aspects of the bill have already been filed in courts, signaling that legal scrutiny may delay its full implementation.
Smaller colleges have expressed concerns about the administrative challenges the bill imposes. Setting up Equity Committees, maintaining round-the-clock reporting systems, and submitting regular compliance reports may strain already limited institutional resources, leaving some institutions worried about penalties despite their best efforts. Experts also warn that without clear safeguards, the regulations could inadvertently create divisions among students and faculty, potentially undermining the very goals of inclusion and fairness that the bill seeks to achieve.
Despite the controversy, the government has assured that the UGC Bill 2026 will be implemented within constitutional limits and that no one will be unfairly targeted. Oversight mechanisms, including central monitoring and judicial review, are expected to prevent misuse. Analysts say that the coming months will be critical in determining whether the bill truly strengthens equity in India’s higher education system or becomes a source of campus tension and administrative complications.
The introduction of the UGC Bill 2026 marks one of the most significant and debated reforms in Indian higher education in recent years, highlighting the delicate balance between ensuring inclusion, maintaining fairness, and managing practical implementation challenges across the country’s diverse educational landscape.